Android Studio
Get started adding Resonance Audio to your Daydream and Cardboard apps in Android Studio.
This guide helps you set up your development environment and tour the Resonance Audio features used in a sample virtual reality app.
Note: Resonance Audio is packaged as “Google VR Audio” in the Google VR SDK for
Android. Access Resonance Audio capabilities using GvrAudio
components, as shown in this guide.
Set up your development environment
Hardware requirements:
-
Daydream: You’ll need a Daydream-ready phone and a Daydream View.
-
Cardboard: You’ll need an Android device running Android 4.4 ‘Kit Kat’ (API level 19) or higher and a Cardboard viewer.
-
You’ll need headphones to experience the sample app’s spatial audio.
Software requirements:
-
Android Studio version 2.3.3 or higher.
-
Android SDK 7.1.1 ‘Nougat’ (API level 25) or higher.
In Android Studio, go to Preferences > Appearance and Behavior ** > **System Settings > Android SDK to review or update installed SDKs. -
Google VR SDK for Android version 1.80.0 or higher.
Open the Google VR SDK project in Android Studio
-
Extract the downloaded Google VR SDK into a convenient location.
-
Open Android Studio and select Open an existing Android Studio project.
Select the directory where you extracted the Google VR SDK. -
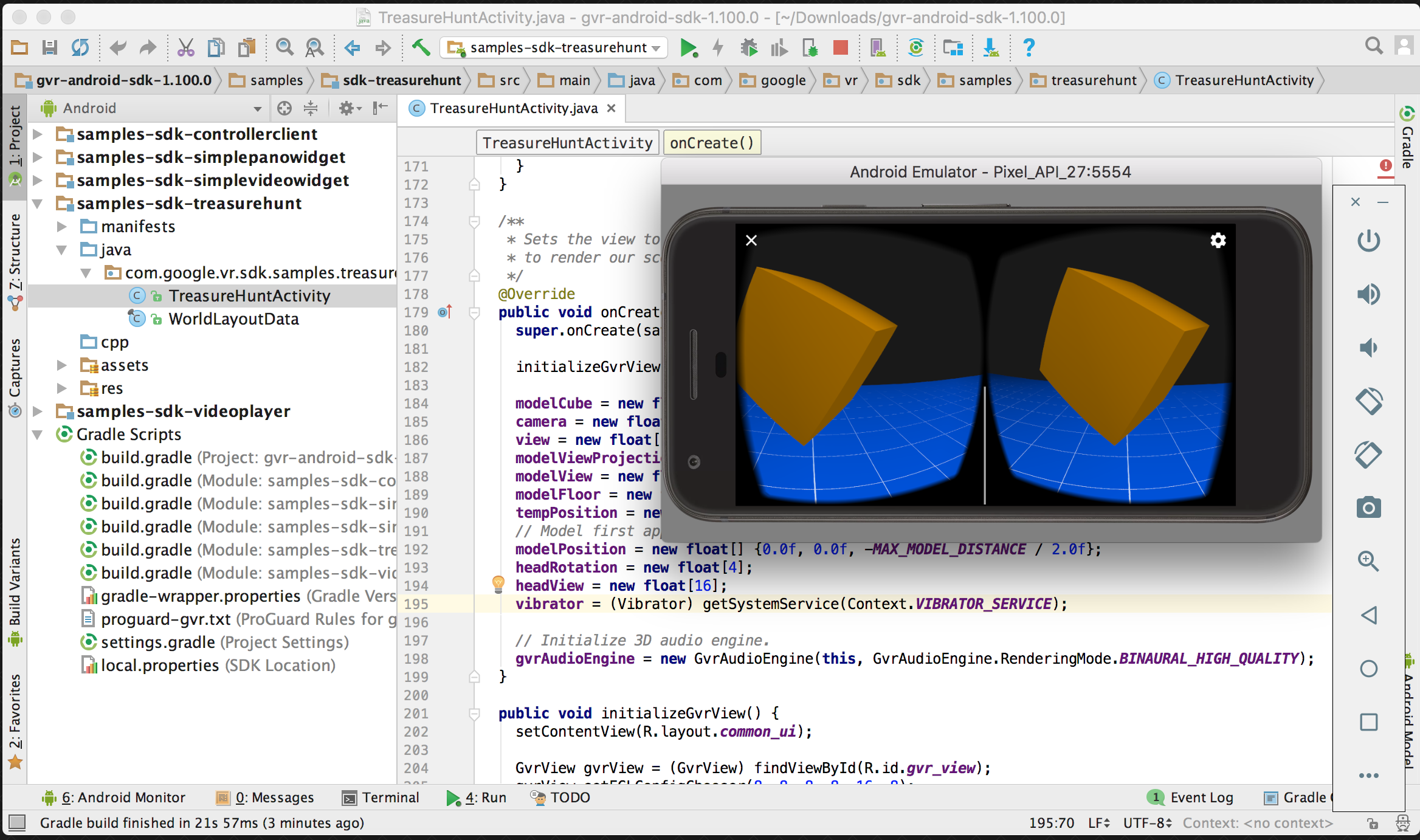
In the Project window, find the sdk-treasurehunt module in gvr-android-sdk > samples.
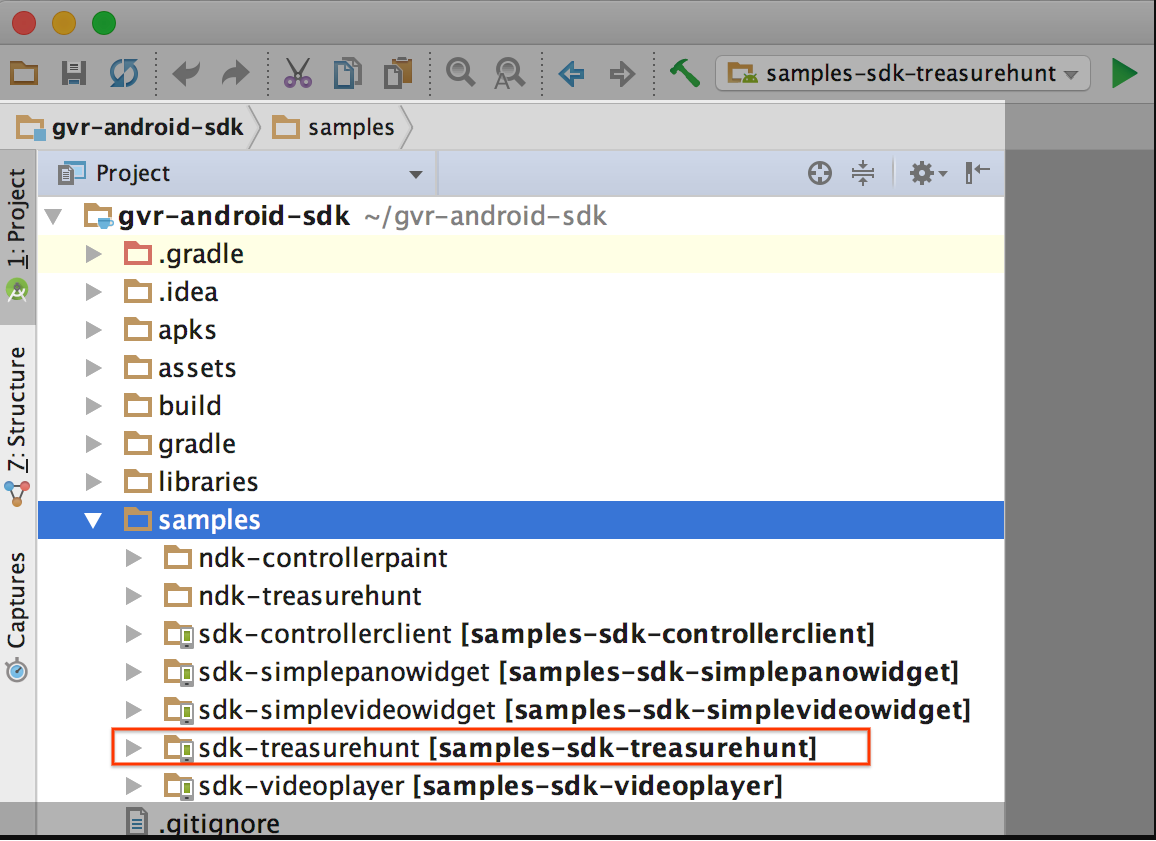
Build and run the sample app
-
Connect your phone to your machine using a USB cable.
-
In Android Studio, select Run > Run… and select the samples-sdk-treasurehunt target. Android Studio compiles and runs the application on your phone.
-
Put your phone into your viewer and use the app. Make sure to wear headphones to experience the app’s spatial audio.
- Look around for the large cube.
- Daydream: Point the controller at the cube and press the touchpad
button to collect it.
Cardboard: Look at the cube and press the Cardboard button to collect it. - The cube moves to a new location after a button press.
How Resonance Audio works in the sample app
The Treasure Hunt app uses Resonance Audio to render realistic spatial audio.
You can walk through the TreasureHuntActivity code in the sample app to
explore the Resonance Audio API.
Open the source code in Android Studio
- To start exploring the code, navigate to
sdk-treasure-hunt > src > main > java >
com.google.vr.sdk.samples.treasurehunt >
TreasureHuntActivity
Initializing the audio engine
The Resonance Audio engine is initialized in the TreasureHuntActivity
onCreate() method.
gvrAudioEngine =
new GvrAudioEngine(this, GvrAudioEngine.RenderingMode.BINAURAL_HIGH_QUALITY);
Note that the audio engine constructor lets you specify a rendering quality mode.
Pausing and resuming audio
TreasureHuntActivity handles app pause or resume
events in onPause() and onResume. Within these methods,
the Resonance Audio engine also pauses and resumes.
Preloading sound files
Sound files can be streamed during playback or preloaded into memory before playback.
Perform preloading in a separate thread in order to avoid blocking the main thread.
new Thread(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// Preload the sound file
gvrAudioEngine.preloadSoundFile(SOUND_FILE);
}
})
.start();
Creating, positioning, and playing audio for sound objects
In TreasureHuntActivity, a sound object represents spatial audio for the
moving cube that users look for and collect.
The same thread used for preloading the sound file in
TreasureHuntActivity is used for setting up the sound object:
public void onSurfaceCreated(EGLConfig config) {
[...]
new Thread(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// Preload the sound file
gvrAudioEngine.preloadSoundFile(SOUND_FILE);
// Create the 'sourceId' sound object.
// You can create multiple sound objects using the same sound file.
sourceId = gvrAudioEngine.createSoundObject(SOUND_FILE);
// Set the sound object position relative to the room model.
gvrAudioEngine.setSoundObjectPosition(
sourceId, modelPosition[0], modelPosition[1], modelPosition[2]);
// Start audio playback of the sound object sound file at the
// cube model position. You can update the sound object position
// whenever the cube moves during run time.
gvrAudioEngine.playSound(sourceId, true /* looped playback */);
}
})
.start();
}
Making the sound object respond to model and user head movements
In TreasureHuntActivity, when the cube moves during run time, the
sound object that represents the cube audio moves with it.
protected void updateModelPosition() {
[...]
// Update the sound location to match the new cube position.
if (sourceId != GvrAudioEngine.INVALID_ID) {
gvrAudioEngine.setSoundObjectPosition(
sourceId, modelPosition[0], modelPosition[1], modelPosition[2]);
}
On each frame update, TreasureHuntActivity gets the latest user head position
quaternion and passes it to the audio engine for rendering the sound
object’s spatial audio.
public void onNewFrame(HeadTransform headTransform) {
[...]
// Update the 3d audio engine with the most recent head rotation.
headTransform.getQuaternion(headRotation, 0);
gvrAudioEngine.setHeadRotation(
headRotation[0], headRotation[1], headRotation[2], headRotation[3]);
//Update the GVR Audio engine on each frame update.
gvrAudioEngine.update()
}
Using the Resonance Audio SDK in your own projects
To use Resonance Audio in your own projects, set up dependencies.
If you are using ProGuard in your app, add rules to ensure that it does not obfuscate any SDK code.
Setting up Resonance Audio dependencies
- Configure your project level build.gradle file:
- Make sure that the default
jcenter()repository location is declared. -
Declare an Android Gradle plugin dependency:
Google VR SDK projects: Usegradle:2.3.3or higher.
Google VR NDK projects: Usegradle-experimental:0.9.3or higher.allprojects { repositories { google() jcenter() } } dependencies { // The Google VR SDK requires version 2.3.3 or higher. classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:2.3.3' // The Google VR NDK requires experimental version 0.9.3 or higher. // classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle-experimental:0.9.3' }
- Make sure that the default
-
Add Resonance Audio to other dependencies in your module level build.gradle files. As an example, review the
dependenciesdeclared for the Treasure Hunt app in gvr-android-sdk > samples > sdk-treasurehunt > build.gradle.dependencies { // Adds Google VR spatial audio support compile 'com.google.vr:sdk-audio:1.80.0' // Required for all Google VR apps compile 'com.google.vr:sdk-base:1.80.0' }For more information, see Add Build Dependencies in the Android Studio guide.
Configure ProGuard
If you are using ProGuard to minimize your app’s APK file, make sure that ProGuard does not obfuscate any Google VR SDK or NDK code. This makes it easier to debug stack traces in release builds.
Add the Google VR ProGuard proguard-gvr.txt rules to your module level build.gradle file:
android {
...
buildTypes {
release {
minifyEnabled true
proguardFiles.add(file('../../proguard-gvr.txt'))
}
}
}
Next Steps
-
Review the Resonance Audio API reference documentation for complete details on Resonance Audio capabilities that you can use in your own projects.